Laser cutting is a revolutionary technique that has transformed manufacturing, crafting, and design by enabling precise, efficient, and intricate cuts that were previously difficult or impossible with traditional tools. At Maker Cube in Langley BC, we leverage this precise and versatile tool to empower makers and creators in our community. I’ll walk you through the essentials of laser cutting, from how it works to its applications, costs, and advantages.
Why Laser Cutting Is Our Favorite Tool
By Doug Chan
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a high-precision thermal process that uses a focused laser beam to cut, engrave, or shape materials. This method is known for its ability to produce intricate designs and high-quality finishes with minimal waste. Whether you’re working with metals, wood, or plastics, laser cutting is a versatile solution for creating professional-grade results.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
Understanding the steps of laser cutting is crucial for achieving optimal results and appreciating the technology’s precision. Laser cutting involves several key steps that make it both efficient and accurate:
Beam Generation
A laser resonator generates a focused beam of light in the infrared spectrum, effectively functioning as a heat laser. Most common hobby-level machines use a glass CO₂ tube to produce this beam. This concentrated energy is the foundation of the cutting process.
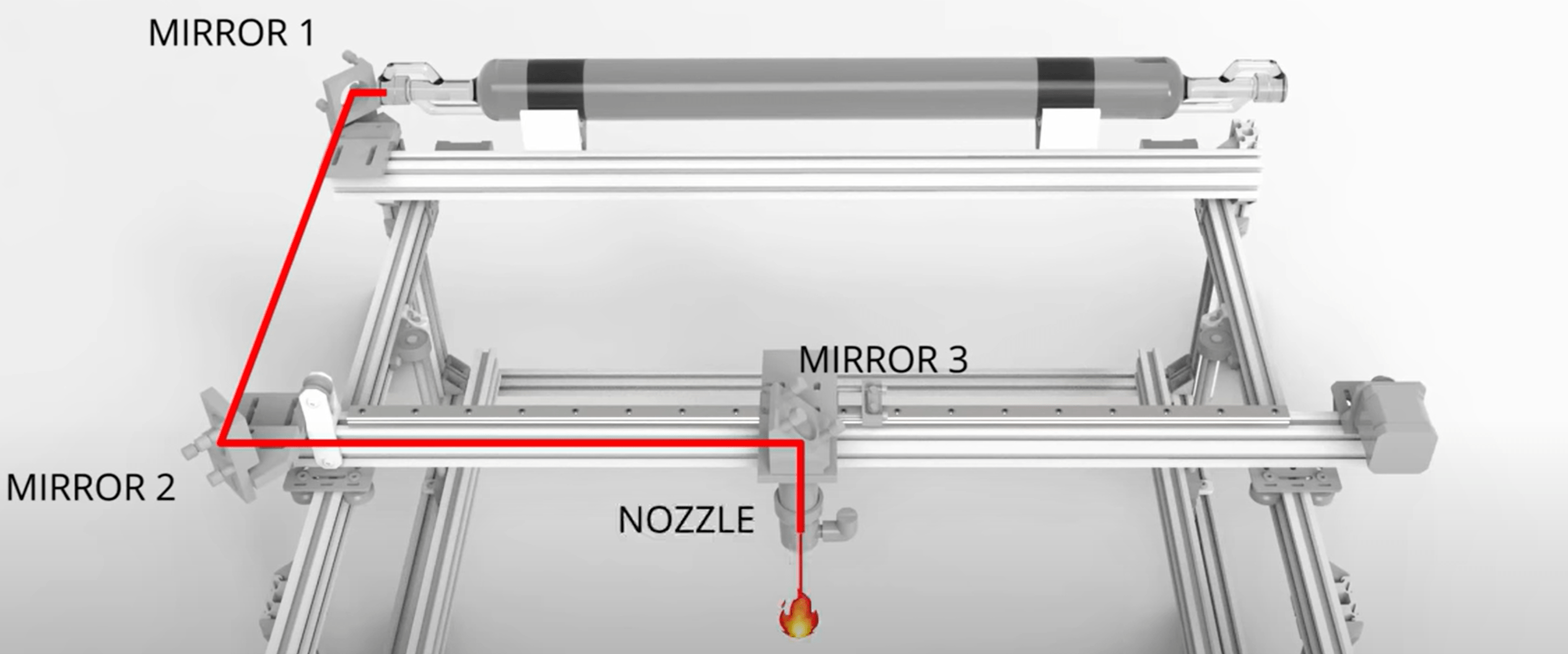
Beam Movement
Since the beam generators are quite large and fixed, the beam is directed around the cutting area by moving mirrors on a large gantry or rotating mechanism. A computer numerical control (CNC) system guides the laser along precise paths, enabling intricate and repeatable cuts. Assist gases like oxygen or nitrogen expel molten material, ensuring clean edges.
Beam Focusing
The beam is focused to a high-intensity spot using lenses, creating a powerful heat source capable of melting or vaporizing materials. Using lenses with different focal lengths can provide either deeper cutting profiles or more accurate engravings.
Localized Heating
The intense heat melts or vaporizes the material along a defined path, following a design programmed into the machine. Assist gases like oxygen or nitrogen expel molten material, ensuring clean edges.
To learn more about the optical physics of how laser cutters operate this video by BuildYourCNC has a great explanation.
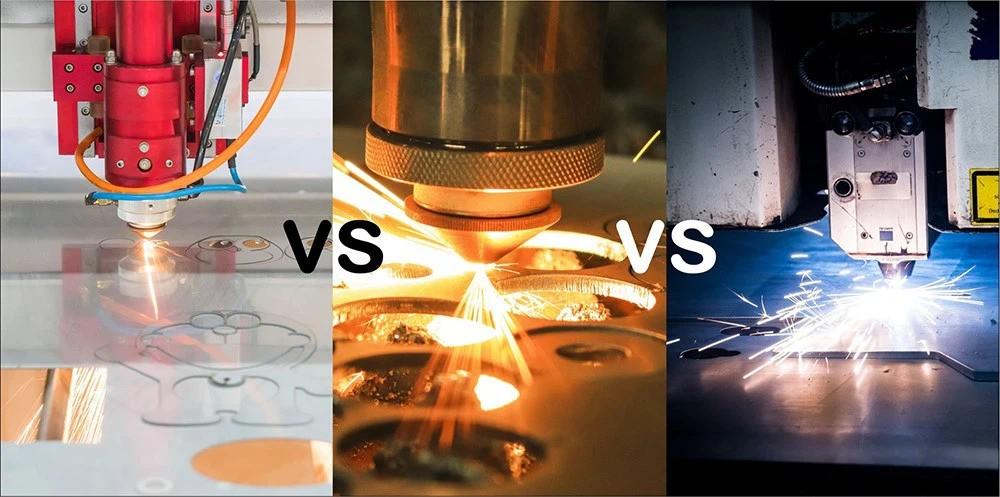
Types of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting can be categorized into various types, each tailored to specific needs. These categories differ in their energy sources and applications, allowing for a broad range of materials and uses:
CO₂ Lasers
Ideal for cutting non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, and textiles. These are the most common types of lasers for hobbyists due to their affordability and versatility in working with a wide range of non-metallic materials. They are less effective on metals but can sometimes engrave coated metals.
Nd and Nd\:YAG Lasers
Perfect for high-energy applications such as cutting thick metals or deep engraving. While primarily used for metallic materials, they can also process some non-metallic materials, though this is less common. These lasers are more expensive than CO₂ lasers due to their higher power and specific applications.
Fiber Lasers
Efficient for cutting reflective materials like aluminum and copper. They are highly specialized for metals and are generally not used for non-metallic materials. Fiber lasers tend to be the most expensive of the three types, often reserved for industrial applications requiring precision with reflective metals.

Materials Suitable for Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is compatible with a wide range of materials:
Metal
Thin sheets of stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals can be precisely cut. However, cutting metals often requires a much higher power laser and may need the support of shielding gases or pure oxygen fed into the cutting zone to enhance the process.
Wood
From plywood to hardwood, laser cutting offers smooth and detailed results. At Maker Cube in Langley, BC, this is the most popular use for our laser cutters as it complements woodworking projects exceptionally well. Members often use laser cutting to add one-off embellishments or create templates that make their woodworking projects easier and more precise.
Plastics and Miscellaneous Materials
Materials like acrylic, polyester, PET, and EVA foam can be cut cleanly with laser technology. However, certain synthetic and petroleum-based products should not be cut, as burning them can produce toxic or corrosive gases.
Applications of Laser Cutting
For a closer look at the variety of projects made possible with laser cutting, check out our portfolio of projects. Laser cutting is used across industries, from manufacturing to arts and crafts. Here are a few examples of projects we’ve done at Maker Cube to showcase the variety of what can be made and the time it takes to complete them:
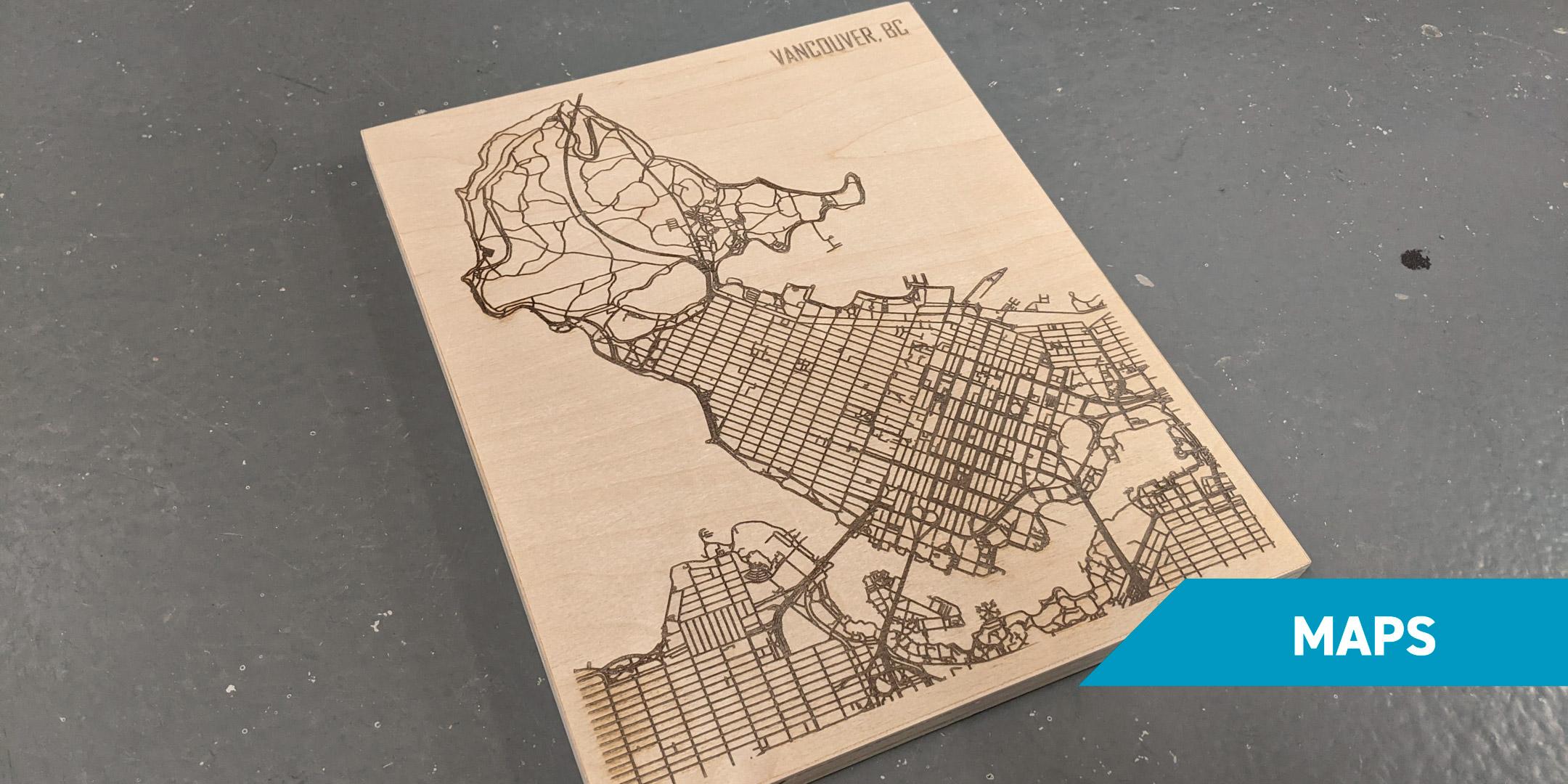
- Laser Engraved Maps: A 10×10” map takes approximately 20 minutes to engrave. These can be easily customized and engraved on canvases or other materials, making them perfect for personalized gifts or decor.
- Small Organizer Boxes: Depending on the size, these boxes are quick to produce. For instance, a 3x3x3” box with a lid takes about 4 minutes to cut using 1/8” material. They’re great for organizing small items and are a hit among crafters.
- Lettering for Signage: We’ve created 4” tall letters for signage using a specialty material with adhesive backing. These were approximately $12 per letter and are ideal for creating professional-looking signs for businesses or events.
Laser cutting is used across industries, from manufacturing to arts and crafts:
Cutting
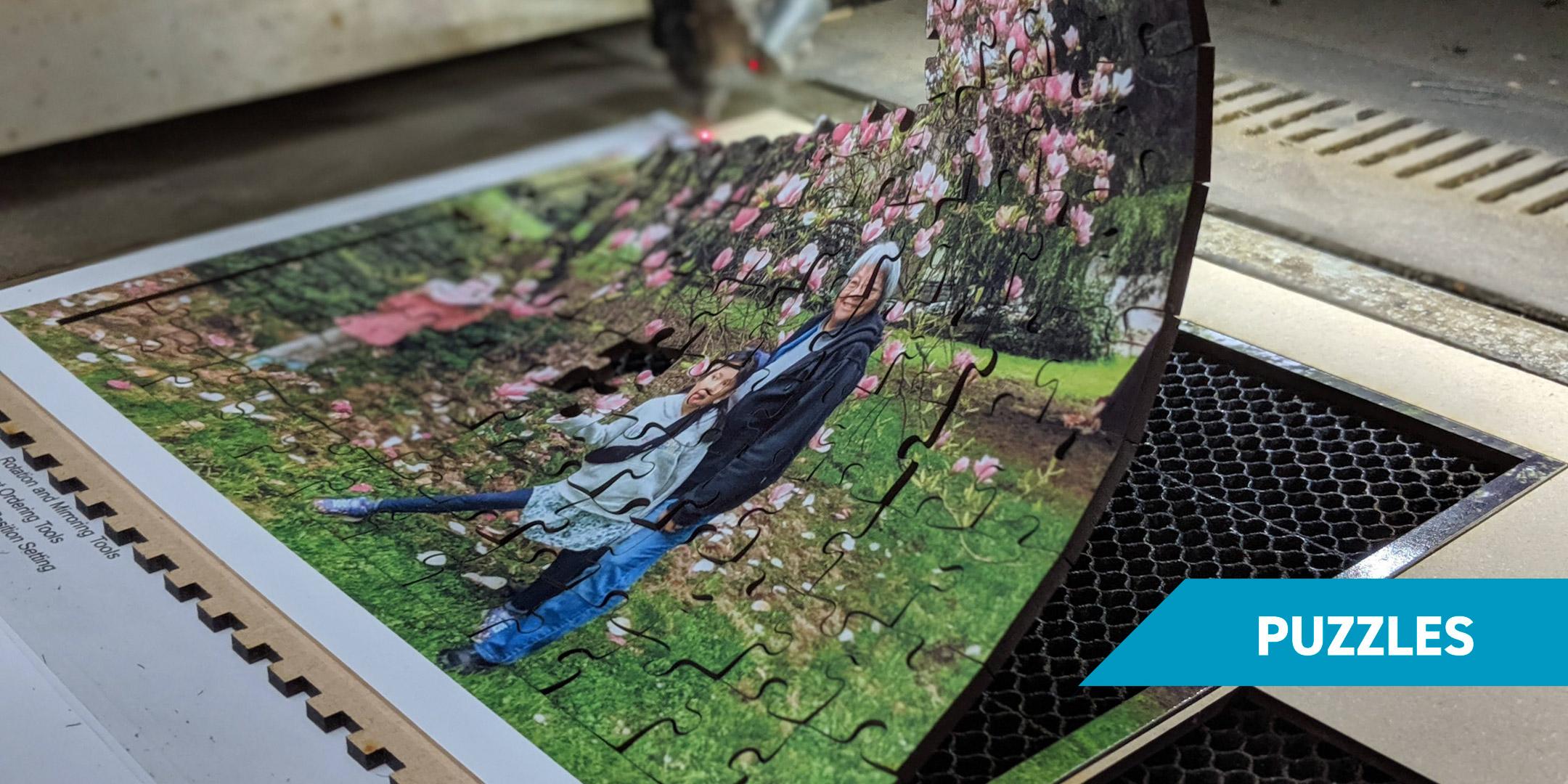
Laser cutting achieves exceptional precision with a minimal kerf, enabling the production of intricate internal cuts, sharp corners for features like finger joints, and patterns like live hinges. The maximum cut depth depends on the material’s thickness and density. For example, composites such as MDF and plywood typically work best below 1/4″ when using CO₂ lasers, while solid materials like acrylic and solid wood can be cut up to 1/2″. Additional examples include creating geometric designs for intricate jewelry, detailed stencils for painting or etching, and functional components such as interlocking parts for furniture or prototypes.
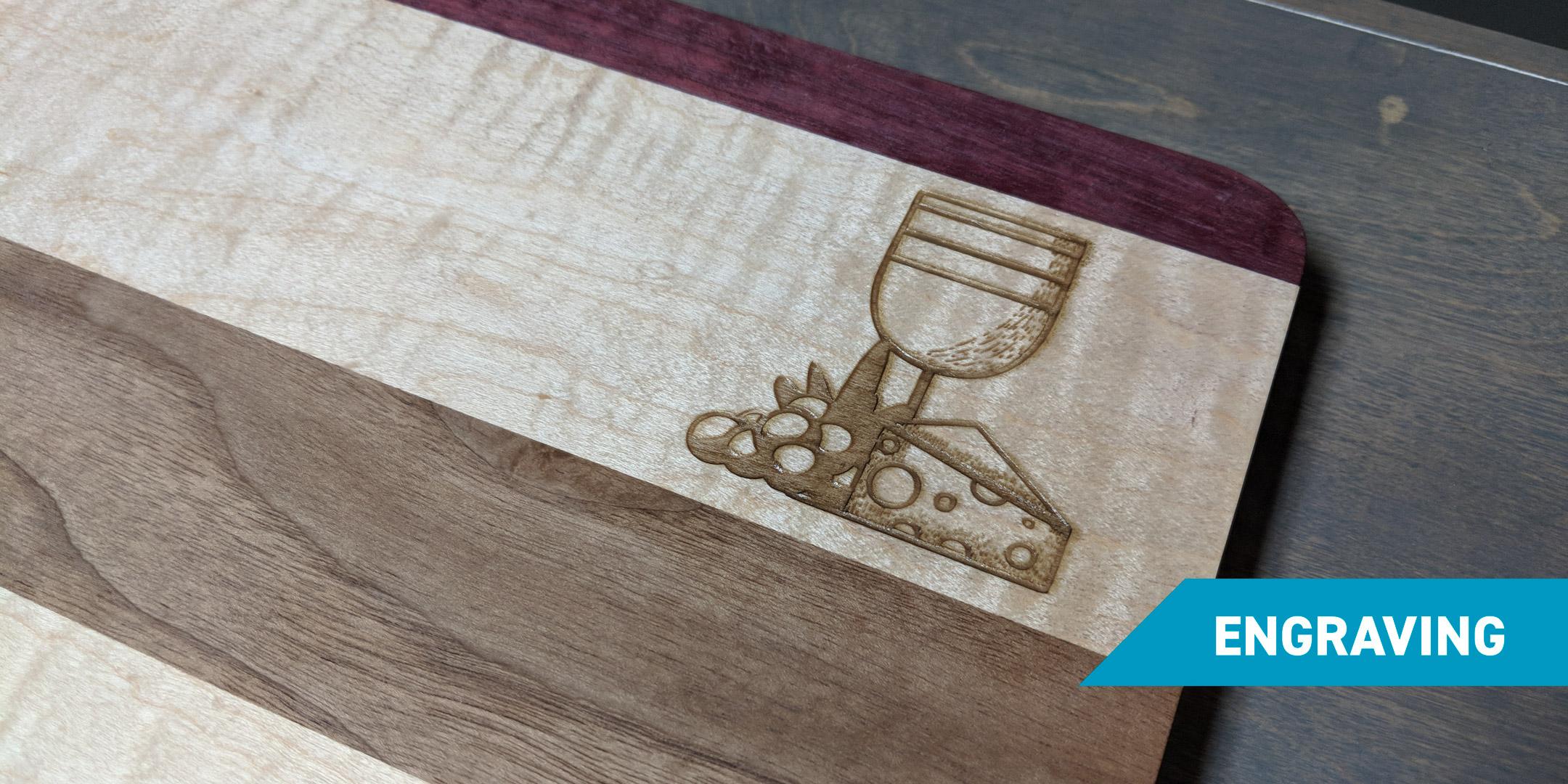
Marking and Engraving
Laser cutting is also ideal for engraving logos, serial numbers, or artistic designs on various surfaces. This application is widely used in branding, personalization, and industrial identification. For example, engraved designs on metal and wood are popular for creating custom awards, nameplates, and decorative items. Serial number engraving is critical for product traceability in industries like manufacturing and medical devices.

Cost and Equipment
How Much Does Laser Cutting Cost?
The cost of laser cutting varies based on factors such as material type, thickness, and project complexity. For example, cutting thin wood or acrylic might cost as little as $1 per minute, while intricate metal designs can range between $3 to $5 per minute depending on the material and setup requirements. At Maker Cube, we offer competitive pricing tailored to your needs.
How Much Does a Laser Cutting Machine Cost?
Laser cutting machines range from affordable models for hobbyists to high-end industrial systems. Hobby tabletop machines like the Glowforge typically range between $2,000 to $5,000. Standalone machines with larger bed areas, such as Boss, Thunderlaser, Rabbitlaser, Redsail, and Omtech, range between $5,000 to $15,000. Higher-end machines produced domestically, like Trotec and Epilog, may cost $20,000 to $30,000.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting
Benefits of Laser Cutting
- High precision for intricate designs.
- Minimal material waste.
- Clean, sealed edges requiring little post-processing.
- Compatibility with a wide range of materials.
Limitations and Challenges
- High initial equipment costs.
- Power consumption.
- Challenges with reflective materials like aluminum.

FAQs About Laser Cutting
What materials can be cut with laser cutting?
Laser cutting works with metals, wood, plastics, and textiles, making it versatile for many applications.
How accurate is laser cutting?
Laser cutting offers extremely high precision, allowing for intricate designs with minimal error margins. Typical tolerances are within ±0.5mm but can be affected by the focus and thickness of the material.
Is laser cutting expensive?
While initial equipment costs are high, the operational costs are reasonable, especially for large-scale or repetitive projects.
Can Maker Cube help me with laser cutting?
Yes! Maker Cube provides access to laser cutting tools and resources for hobbyists and professionals. We also offer workshops and support for learning the technique. Click here to see upcoming workshops.
Do I need prior experience to use laser cutters at Maker Cube?
No prior experience is necessary. Our team will guide you through the process, ensuring safety and successful results. Click here to learn more about becoming a member and accessing a laser cutter at our Langley, BC location.
Can Maker Cube make something for me?
Absolutely! If you have a design or concept in mind, Maker Cube can help bring it to life. Whether it’s custom signage, intricate engravings, functional prototypes, or personalized gifts, our team and equipment are here to support your vision. Share your ideas with us, and we’ll work with you to create something unique and tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Laser cutting is a game-changer for makers and professionals alike, offering unmatched precision and versatility for a variety of applications. At Maker Cube, we provide the tools, resources, and guidance to help you make the most of this powerful technology. From workshops to hands-on support, our team is dedicated to enabling your creative and professional goals. At Maker Cube, we’re here to help you harness this powerful tool for your projects. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, we provide the equipment, knowledge, and support to bring your ideas to life. Visit us in Langley, Canada, and let’s make something incredible together!